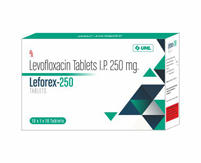
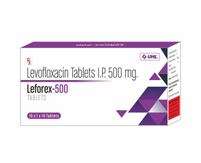
- S. No.Brand NamePackagingComposition
- 1.Leforex 250 Tablet10x1x10Levofloxacin 250mg
- 2.Leforex 500 Tablet10x1x10Levofloxacin 500mg
Mechanism of Action: Levofloxacin functions by inhibiting the DNA replicated (doubled) prior to bacterial cell division. With the DNA not being separated, the process is stopped and the bacterium cannot divide. DNA gyrase, on the other hand is responsible for supercoiling the DNA.
Indications:
- Bacterial infections
- Infections of urinary tract
- Tonsils, sinus & nose
- Female genital organ
- Windpipe & lungs (pneumonia) infections
Dosage:OD to BD